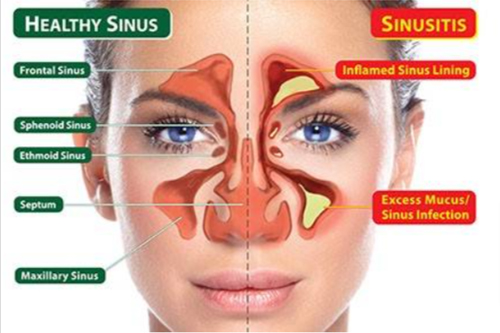
Sinus treatment in Nagpur “sinus” can refer to several different structures in the human body, but it is most commonly use to describe the paranasal sinuses. The paranasal sinuses are a group of air-fille cavities locate in the bones of the skull around the nose and eyes. These sinuses are connecte to the nasal cavity through small openings.
These sinuses are lined with a mucous membrane and are connected to the nasal cavity through small openings called ostia. The purpose of the sinuses is not entirely clear, but they are thought to play a role in humidifying and filtering the air we breathe, as well as in providing structural support to the skull and resonance to the voice.
Types of sinusitis
Acute Sinusitis:
- Acute sinusitis is a short-term inflammation of the sinuses, often cause by a bacterial infection. It usually follows a cold or respiratory infection and lasts for less than four weeks. Symptoms may include facial pain or pressure, nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, and fatigue.
Subacute Sinusitis:
- Subacute sinusitis is a condition that lasts between four and 12 weeks. It may represent a prolonge course of acute sinusitis or a milder form of inflammation. The symptoms are similar to those of acute sinusitis but persist for a more extende period.
Chronic Sinusitis:
- Chronic sinusitis is characterize by persistent inflammation of the sinuses that lasts for 12 weeks or longer. It may be cause by various factors, including infections, nasal polyps, a deviate septum, or allergies. Symptoms often include nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, drainage of thick discharge, and a reduce sense of smell.Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS):
- AFS is a specific type of chronic sinusitis associate with allergic reactions to fungal organisms. It often occurs in individuals with a predisposition to fungal allergies. Symptoms may include nasal polyps, thick nasal discharge, and facial pain.
Fungal Sinusitis:
- Fungal sinusitis includes various types of sinus infections cause by fungal organisms. These infections can be categorize as invasive or non-invasive, and they are more commonly seen in individuals with weakene immune systems.
Ethmoid Sinusitis:
- Ethmoid sinusitis specifically involves inflammation of the ethmoid sinuses, which are located between the eyes and behind the nasal bridge. Symptoms may include pain or pressure between the eyes, nasal congestion, and headache.
Frontal Sinusitis:
- Frontal sinusitis refers to inflammation of the frontal sinuses, which are locate in the forehead above the eyes. Symptoms may include forehead pain, tenderness, and nasal congestion.
What are the Sinus Symptoms
Nasal Congestion:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose due to swelling and blockage of the nasal passages.
Facial Pain or Pressure:
- Pain or pressure in the face, particularly in the forehead, between the eyes, and around the cheeks. The pain may worsen when bending forward.
Headache:
- A dull or throbbing headache, often centered around the forehead and eyes.
Thick Nasal Discharge:
- Yellow or greenish mucus drainage from the nose. The color may indicate the presence of infection, but not all cases of sinusitis involve bacterial infections.
Loss of Smell:
- A reduce or complete loss of the sense of smell (anosmia) can occur with sinusitis.
Cough:
- A persistent cough, especially when the drainage irritates the back of the throat.
Fatigue:
- General fatigue or feeling unwell, especially in cases of acute or chronic sinusitis.
Ear Pressure or Fullness:
- Pressure or fullness in the ears may occur due to the blockage of the Eustachian tubes connecting the middle ear to the back of the throat.
Sore Throat:
- Irritation or soreness in the throat, often associated with postnasal drip.
Bad Breath:
- Foul-smelling breath (halitosis) may be present due to the buildup of mucus and bacteria in the sinuses.
Fever:
- In acute bacterial sinusitis, fever may be present, especially in children.
Treatment of Sinus
Home Remedies and Self-Care:
- Nasal Irrigation: Using a saline nasal rinse or a nasal irrigation system can help clear mucus and reduce nasal congestion.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the face may help relieve facial pain or pressure.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help keep mucus thin and promote drainage.
Medications:
- Antibiotics: If the sinusitis is bacterial in nature, antibiotics may be prescribe to eliminate the infection. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before completion.
- Decongestants: Over-the-counter or prescription decongestants can help reduce nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages.
- Nasal Steroid Sprays: Corticosteroid nasal sprays can reduce inflammation and help control symptoms. They are often use for chronic sinusitis.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Nasal Corticosteroid Sprays:
- Prescription nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone or mometasone, may be recommended to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
Antihistamines:
- If sinusitis is associate with allergies, antihistamines may be helpful in managing symptoms.
Intranasal Saline Irrigation:
- Saline irrigation using a neti pot or a nasal spray can help flush out mucus and irritants from the nasal passages.
Topical Decongestants:
- Topical nasal decongestant sprays, such as oxymetazoline, can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion. However, these should be use for a short duration to avoid rebound congestion.
Allergy Management:
- If allergies contribute to sinusitis, managing allergens through avoidance measures or allergy medications may be recommended.
Surgery:
- In cases of chronic or recurrent sinusitis that does not respond to conservative treatments, surgical interventions may be considere. Procedures may include functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) to remove nasal polyps, correct anatomical issues, or improve sinus drainage.